This is a comprehensive and detailed page that will give you all the information you need to know about all electronic components and their functions. Being the building blocks of modern technology, I have had this thought that electronic components are the unsung heroes of technology. Components do enable the control and therefore the manipulation of electrical signals allowing for the creation of a wide range of electronic systems and devices.
These could be simple electronic circuits like the ones found on remote controls or even complex microprocessors that are found in computers. This page will also act as a guide on all the electronic components that we have at our electronic store in Kenya. Kindly visit our About page and learn more about us. We are the best electronic components store in Kenya and only stock genuine and authentic components at the best prices.
Electronic Components Applications
There are so many applications that emanate from components. Below we share with you three categorizations that we believe capture the various applications. These amazing pieces of technology play a very crucial and critical role in our day-to-day lives and can be utilized to create wonderful applications. Kindly see the three categories below: If we forgot some, do not hesitate to let us know.
Assembly of new and modern appliances and gadgets
Most of the appliances and gadgets you see around or indeed have around you have been assembled and built from components. These tiny and powerful devices are the fundamental building blocks of new and modern-age electronics. Furthermore, they have also enabled the production of appliances and gadgets that have changed our lives very much. Drones, Smartphones, Space Crafts, Smart Cars, IoT, Planes, and supercomputers have all been built using electronic components.
Assembly of DIY (do it yourself) projects
If you are a student or electronic hobbyist, then you can utilize these devices to assemble and make your DIY (do-it-yourself projects) In addition to this, you can also discover new electronic theories with electronic components. And the truth is, you can even become an electronics pro by just learning on the go.
Some of the DIY projects you can undertake would include:
- Rotating solar panels (Using Arduino)
- Arduino ultrasonic radar and sonar monitor project
- Power monitor regenerative braking project
- IoT-enabled notifications smart dustbin
- Autonomous fire-fighting robot
The above are just a tiny fraction of the hundreds of thousands of electronic DIY projects that you can actualize.
Repair of electronic appliances and gadgets
If you own an electronic appliance or gadget, then it is most likely that you have needed it repaired after getting faulty or maintained after serving you for a while. With components, repair, and maintenance of appliances and gadgets is way easier. All you need is a qualified technician or detailed videos and tools and you are set. Furthermore, if doing it yourself, you’ll need to observe the necessary precautions to avoid injury. You can utilize these devices to maintain or repair your DVD, TV, Radio, Playstation, Refrigerator, and many other appliances or gadgets.
Electronic Components Categories
There are two major/ main categories of electronic components which are active components and passive components. Below we delve in and explain to you the difference between the two.
Active Components have some electronic gain and an electronic directionality as well. In addition, their electronic functionality is also defined.
Some examples of active components include:
- Transistors
- Integrated circuits (ICs)
- Logic gates
- Regulators, and
- Relays
Passive components on the other hand do not have a defined directionality and form a majority of the electronic components. Additionally, they do not achieve any gain and usually perform their functions in combination with other components.
Below are some examples of passive components:
- Diodes
- Resistors
- Inductors
- Capacitors
Types of Electronic Components
Now that we have established electronic components applications and categories, it is time to delve deeper and learn more about the various types of components that fall under each category. By doing this, we shall have a better understanding of components. We have gone ahead and done detailed articles on specific types of components. We shall add links to these articles so that you can read and learn more.
Transistors
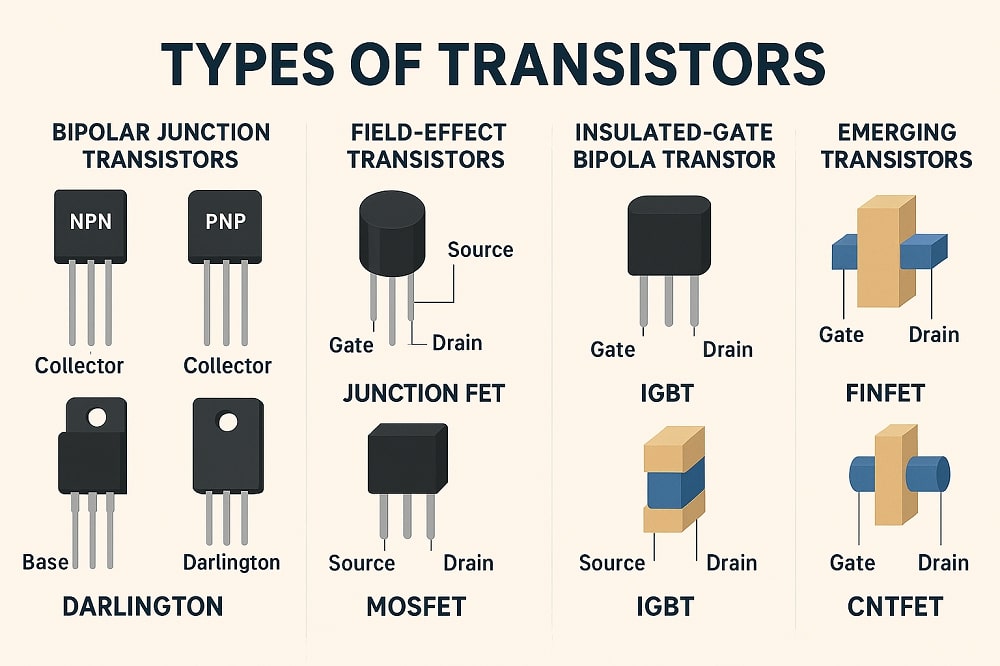
Transistors are important components in the electronic sphere. They have made it possible for us to build simple, complex, and modern devices such as smartphones, drones, computers, radios, and cameras among others. A transistor is a fundamental miniature semiconductor device that controls or regulates voltage and current within an electronic circuit. As this happens, a transistor does some crucial electronic functions like amplification, switching, and signal processing among other functionalities.
Structurally, a transistor contains three layers with each having a terminal attached to it. They are the collector, the base, and the emitter. Each of these terminals is attached to an electronic circuit and has its functionality depending on where and how it is utilized within the circuit. In addition, transistors are categorized into two main types – Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) and Field Effect Transistors (FETs).
How to Choose a Transistor
To select a transistor, begin by choosing between BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) or MOSFET, depending on whether current or voltage control is more suitable. For BJTs, key parameters include collector current (Ic), collector-emitter voltage (Vce), gain (hFE), and switching speed. For MOSFETs, focus on drain current (Id), drain-source voltage (Vds), and gate threshold voltage (Vgs(th)). RDS(on) is crucial in power MOSFETs as it affects conduction losses. Also, consider the package type and thermal resistance for heat dissipation. If you need high gain and high current handling in a compact form, Darlington pairs are ideal. For high-frequency or low-noise applications, opt for JFETs or HEMTs. Always match your transistor’s parameters with your load and driving signal characteristics.
Kindly check out our types of transistors page to learn and know more about these amazing electronic devices. In addition, our transistors store has a wide variety of transistors.
Integrated Circuits ICs
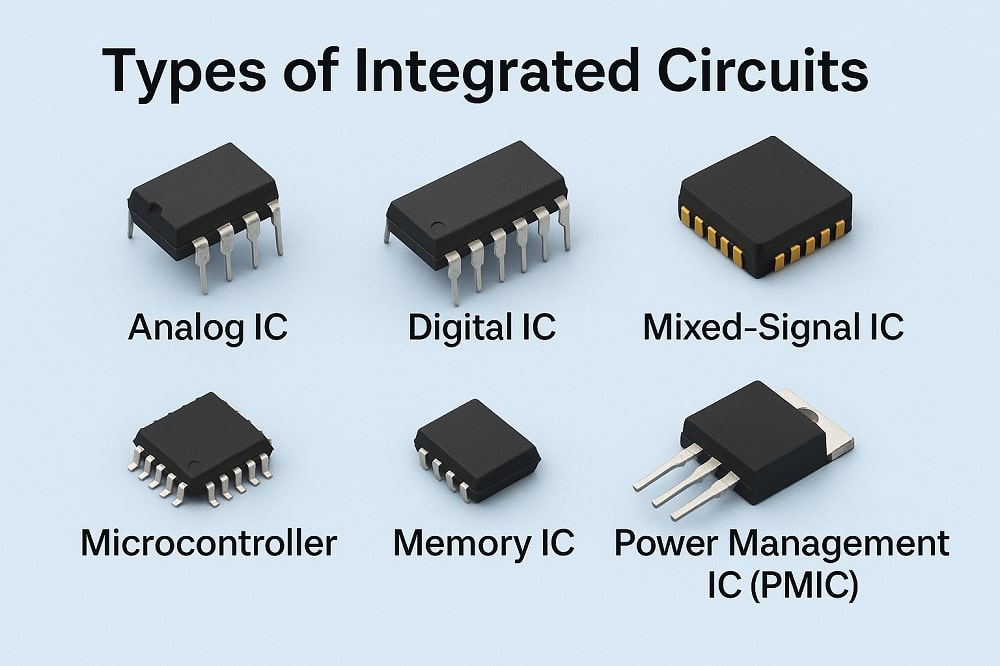
Known as microchips or chips, integrated circuits or ICs are vital and extremely important components in the electronics sphere. They are miniature electronic circuits containing vast numbers of interconnected components like transistors, diodes, capacitors, and resistors among others. All these are contained in a semiconductor substrate making ICs some of the most efficient and easy to work with components.
You can utilize integrated circuits in different electronic applications like in the manufacturing of different electronic devices and electronic systems. Additionally, these amazing electronic components are compact and efficient therefore reliable for different electronic applications. Integrated circuits come in different categorizations and types. Below we highlight some of the most common types.
- Analog Integrated Circuits
- Digital Integrated Circuits
- Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits
- Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits
- Power management ICs – and many more
How to Choose an Integrated Circuit (IC)
Choosing an IC depends entirely on function—whether it’s an amplifier, timer, microcontroller, voltage regulator, or logic gate. First, define the functionality and performance parameters such as operating voltage, supply current, input/output compatibility, and timing characteristics. For analog ICs like op-amps, consider gain bandwidth, slew rate, input offset voltage, and noise level. In digital ICs, check logic family (TTL, CMOS), fan-out, and clock frequency. For microcontrollers, assess memory size, I/O pin count, ADC/DAC resolution, and peripheral support (I2C, SPI, UART, PWM, etc.). Thermal and packaging constraints (DIP, SOIC, QFN, etc.) must align with your PCB design and soldering method. Always verify availability, cost, and community support, especially for programmable ICs.
Kindly visit our types of integrated circuits page to learn more… We are also stockists of integrated circuits. Visit our integrated circuits store and see all the available ICs.
Capacitors
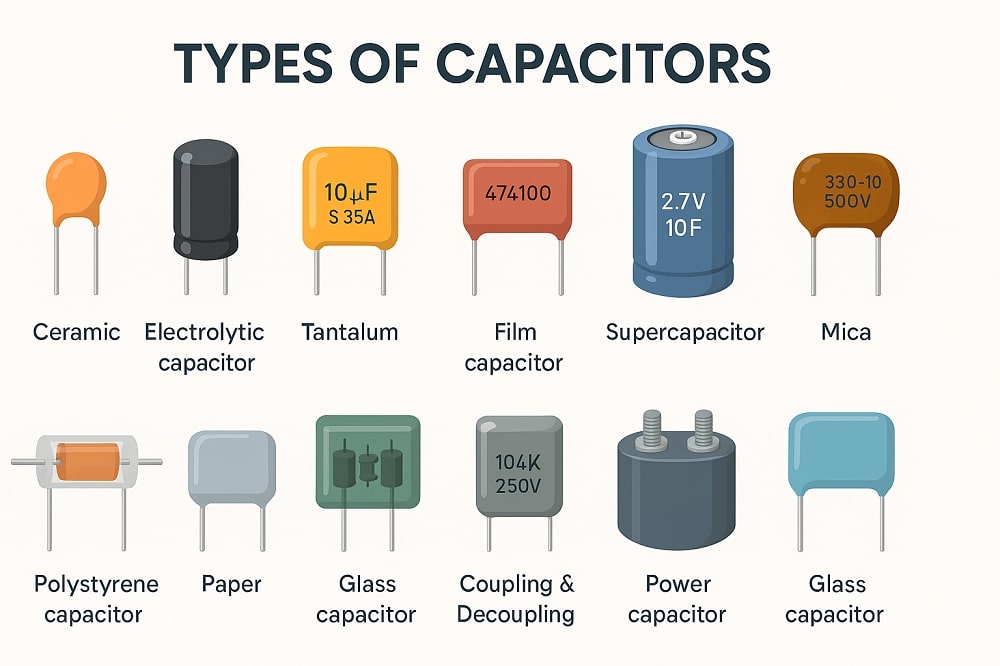
Coming in different types, capacitors are vital components that are used to store electrical charge in an electric field with the effect being known as capacitance. Capacitors being passive components are used in electronic circuits in combination with other components to achieve certain electronic functionalities.
There are four capacitor categories namely – fixed capacitors, variable capacitors, polarized capacitors, and non-polarized capacitors. Some of the types that fall under the above categorizations are:
- Film Capacitors
- Ceramic Capacitors
- Aluminium Electrolytic Capacitors
- Mica Capacitors
- Tantalum Capacitors, among others
In addition to the above, these miniature components have different functionalities depending on their types. They include:
- Energy Storage
- Sinal Coupling
- Motor starting
- Tuning
- Timing
- Decoupling, among others
How to Choose a Capacitor
To select a capacitor, start by identifying the required capacitance value (in microfarads, nanofarads, or picofarads) and the voltage rating, which should always exceed the highest voltage the capacitor will face. Consider the type of capacitor: electrolytic capacitors are excellent for bulk storage and filtering in power supplies but have polarity and limited lifespan; ceramic capacitors are non-polarized and work well for high-frequency bypass and decoupling tasks. Film capacitors are suitable for audio and precision timing due to their stability and low distortion. Also evaluate the Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and temperature stability, especially in switching power supplies and RF circuits. Physical size and mounting style (SMD or through-hole) should align with your PCB design and space constraints.
Kindly visit and have a look at our types of capacitors page and learn everything about capacitors… Additionally, our capacitors store has an array of different types of these components.
Resistors
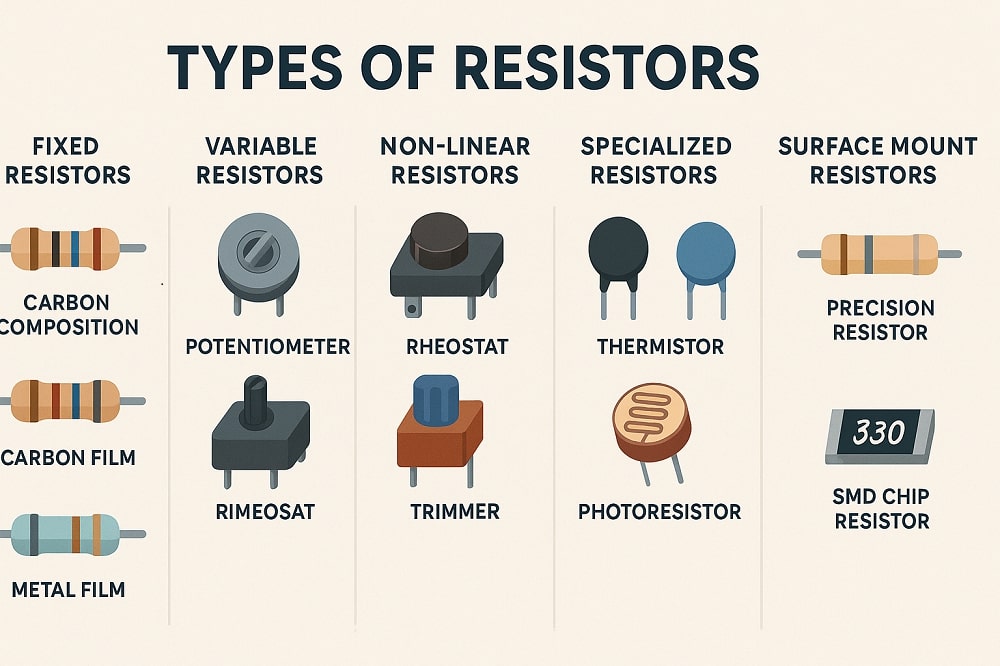
Resistors are essential passive components used in nearly all electronic circuits. Their primary function is to resist or limit the flow of electric current, helping to control voltage levels, protect sensitive components, and shape signal behavior in both analog and digital systems. They are used in everything from power supplies and amplifiers to sensors and LED lighting.
Structurally, a resistor is made of a material with known resistance and has two terminals for connecting to a circuit. The amount of resistance is measured in ohms (Ω) and determines how much the resistor slows down the current flow. When current passes through a resistor, electrical energy is converted into heat, which is a byproduct of its operation.
There are two main categories of resistors: fixed and variable. Fixed resistors provide a constant resistance, while variable resistors, such as potentiometers and rheostats, allow adjustment of resistance based on the application’s needs. Beyond these, there are specialized types like thermistors (temperature-sensitive), light-dependent resistors (LDRs), varistors (voltage-sensitive), high-power resistors, and surface-mount resistors (SMDs). Resistors play a critical role in tasks such as current limiting, voltage division, timing, filtering, and signal conditioning. Compact, reliable, and easy to use, resistors remain one of the most fundamental components in modern electronics.
How to Choose a Resistor
When selecting a resistor, the first and most critical parameter is the resistance value, determined by Ohm’s Law depending on your circuit requirements. Beyond this, consider the power rating (measured in watts)—this must be higher than the actual power the resistor will dissipate to avoid overheating. Tolerance is also vital; for precision circuits, use resistors with tighter tolerances (±1% or better). Also, factor in the temperature coefficient, especially in high-precision or temperature-sensitive applications. Choose the type—carbon film, metal film, wire wound, or surface mount (SMD)—based on the required accuracy, frequency response, and form factor. For example, wire wound resistors are best for high-power applications, while metal film resistors are ideal for low-noise environments.
Kindly visit our resistors store and shop for the resistors you need for your electronic requirements. Additionally, we have a types of resistors page that has all the resistor information that you could be looking for…
Diodes
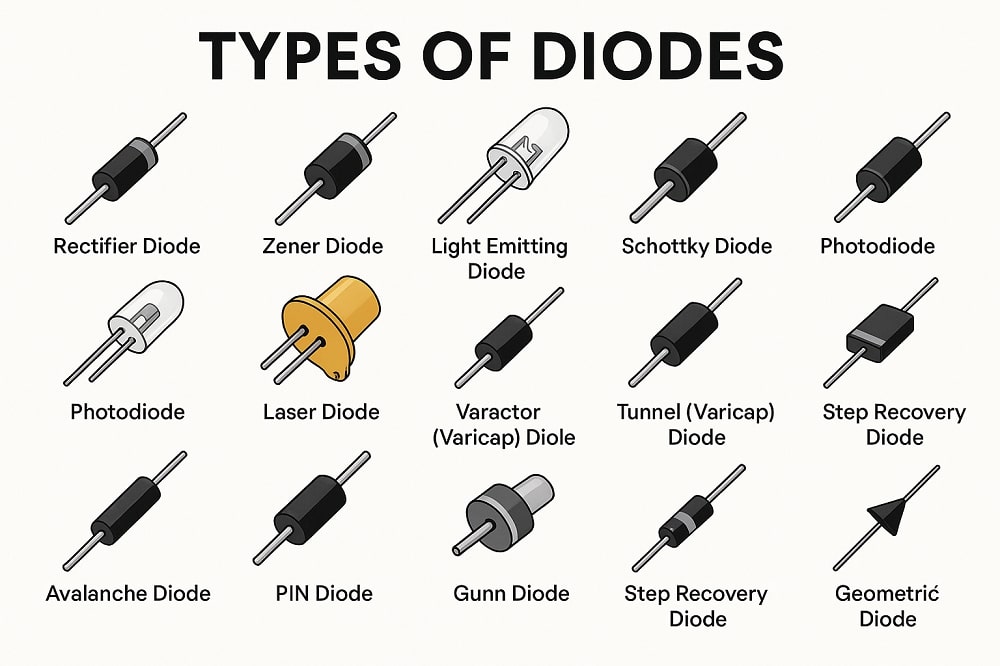
Diodes are fundamental electronic components that play a critical role in modern electronics. These components are used in a wide range of devices, from power supplies and signal modulators to lighting systems and communication equipment.
A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device that allows electric current to flow in only one direction. This property makes it invaluable for controlling the direction of current in a circuit, protecting sensitive components, and converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Structurally, a diode consists of a p-n junction, formed by joining a p-type (positive) and an n-type (negative) semiconductor. The two terminals are known as the anode (connected to the p-type region) and the cathode (connected to the n-type region). When a positive voltage is applied to the anode relative to the cathode, the diode conducts electricity—this is known as forward bias. In the reverse case, it blocks current—called reverse bias.
Diodes are widely used for rectification, voltage regulation, signal demodulation, switching, and light emission, among other applications. There are various types of diodes, each suited for specific functions. Some of the most common include:
- Standard (Rectifier) Diodes
- Zener Diodes
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
- Schottky Diodes
- Photodiodes
- Varactor Diodes
- Tunnel Diodes
Each type has unique characteristics tailored for applications like voltage regulation, high-speed switching, light emission, and signal detection. Diodes are compact, reliable, and energy-efficient components that are essential in both analog and digital electronics. Whether you’re designing power supplies or communication circuits, understanding diodes and their types is key to creating effective electronic systems.
How to Choose a Diode
Choosing the right diode depends on your application—rectification, switching, protection, or light emission. For general rectification, focus on the forward current rating and reverse voltage; these should exceed the peak current and voltage expected in the circuit. Also, the reverse recovery time is critical in high-speed switching applications like SMPS, where fast recovery diodes or Schottky diodes are preferred due to their low forward voltage drop and quick response. For voltage regulation, choose Zener diodes with a breakdown voltage matching your desired reference. In protection circuits, use TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) diodes rated for the specific clamping voltage and peak pulse current. And if you’re using LEDs, consider the forward voltage, current rating, and brightness/lumen output in addition to color and package type.
We wrote a comprehensive and detailed article on all the types of diodes. In addition, our diodes store has a wide selection of diodes that you may be looking for.
Kindly visit our shop and get to see all the electronic products we have in stock. We have gone a step further to review them so that you learn more about them.

